
When someone makes a purchase, a process unfolds that covers different phases from the moment a person seeks to fulfill a need until they finally do so by acquiring a product or service. This is called the Customer Journey.
If you want to learn more about this buying process, its phases, how it can help your business, and the most important social metrics for the Customer Journey, keep reading.
Customer Journey: Definition and Functions
The Customer Journey is what we know in Spanish as the “customer journey,” and it’s the set of phases a person goes through until they become a customer of a product or service. This process can be longer or shorter depending on the product in question. It can also vary depending on the company offering it and the market or sector it’s in.
As we can see, the customer journey is a marketing strategy used to define the buying process for a product or service and recognize the possible needs a potential customer may have during that process.
Being aware of the stages a customer goes through is very useful for designing a successful buying experience that ultimately boosts later loyalty.
Phases of the Customer Journey
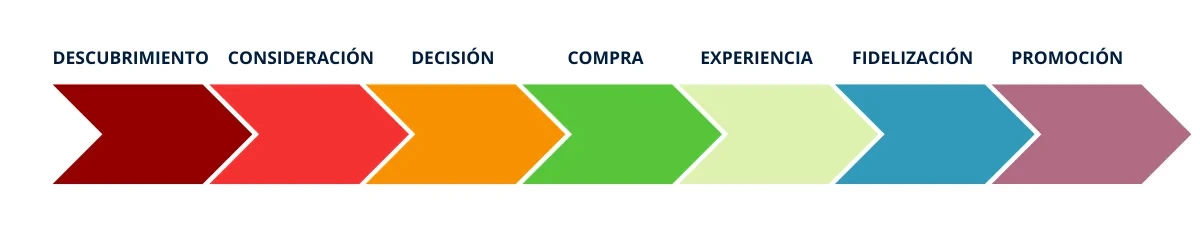
Within the process a consumer goes through when making a purchase, we can distinguish about seven phases. If you’re familiar with the sales funnel or conversion funnel, you’ll probably see that these are two closely related concepts; however, the customer journey is more focused on the customer’s point of view.
These are the main stages a person goes through until they become a final customer:
– Discovery. In this first stage, the customer becomes aware of the existence of a brand and the products or services the company can offer. They may realize these could meet some of their needs. The company, in turn, must make a good impression and provide clear information about what it offers to attract the potential customer.
– Consideration. In this phase, the customer evaluates and compares different options. They often read reviews, look for more data, or ask for recommendations from people they know, among other things. The business at this point should try to demonstrate the value it offers and highlight its differences from the competition.
– Decision. After the previous stage, the potential customer decides to obtain the product or service, considering factors such as price, quality, or brand reputation. The company should offer a simple and secure purchasing process, providing various payment options and return guarantees.
– Purchase. Finally, the person buys the product or service and becomes a customer.
– Usage Experience. While many think the customer journey ends with the purchase, that’s not the case. In this fifth stage, the customer uses the product or service they just acquired. The business should be attentive to any problems or questions the customer may have to provide quality post-purchase support.
– Loyalty. At this point, the customer is already using the product, but if they’ve received good treatment and attention, had a favorable experience, and the company has given them incentives to foster loyalty, it’s likely the customer will become loyal and return for another purchase. For example, a company can offer exclusive discounts to customers.
– Promotion. This is the final stage, and if the customer has had a pleasant process, they often recommend the products or services to people close to them, helping the company reach other potential customers.